

Sirolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System

Next Generation Biodegradable Polymer Technology
Sirolimus-eluting stent featuring a biodegradable polymer and a unique micro-porous PEARL surface, favours better endothelialisation and optimal drug delivery. With 10 years of clinical data, it demonstrates improved long-term performance compared to first-generation DES. The stent’s innovative 2-strut connector design ensures maximum flexibility and optimal side branch access, making it ideal for bifurcation stenting

Sirolimus
A clinically proven immunosuppressant, Sirolimus inhibits T and B cell activation via mTOR inhibition, reducing IL-2 sensitivity. Its anti-proliferative properties prevent restenosis when used with coronary stents.
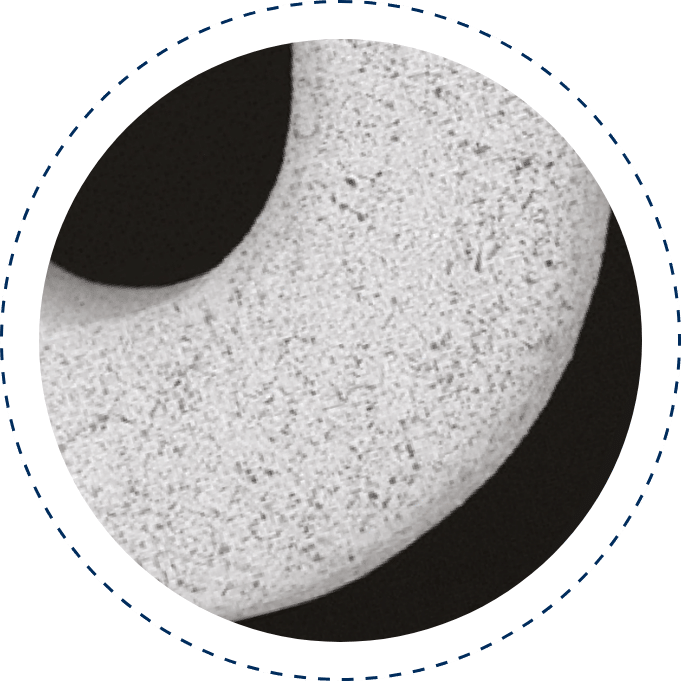
Microporous Surface (PEARL)
The PEARL surface, combined with a biodegradable polymer, enhances endothelialization, reduces restenosis and thrombosis, and ensures controlled drug release, delivering optimal performance as a safe and effective DES technology.

Next-Generation Design
- CoCr platform with thin 68 μm struts for enhanced flexibility and deliverability.
- 2-connector design ensures excellent side-branch access for bifurcation stenting.

Abluminal Coating
Facilitates unidirectional drug release and less systemic exposure, ensuring improved healing & faster endothelialization.
Clinical Studies
10 Years of Robust Data Setting New Standards Longest-Studied DES Technology
![]() In ACS patients, the Yukon stent demonstrated a lower 10-year POCE (65.3% vs. 69% for PP-DES) and a 23% reduced risk of total stent thrombosis.
In ACS patients, the Yukon stent demonstrated a lower 10-year POCE (65.3% vs. 69% for PP-DES) and a 23% reduced risk of total stent thrombosis.
![]() The ISAR-TEST 4 trial’s 10-year follow-up reported the lowest rate of definite/probable stent thrombosis, showing a 50% risk reduction compared to the Cypher stent and a 29% lower rate compared to Xience.3
The ISAR-TEST 4 trial’s 10-year follow-up reported the lowest rate of definite/probable stent thrombosis, showing a 50% risk reduction compared to the Cypher stent and a 29% lower rate compared to Xience.3
![]()
At 10 years, Yukon stent outcomes were comparable to Xience in patients with coronary artery disease, including those with Diabetes Mellitus4, with no significant difference in clinical event rates.
3. Circulation, 138, 00-00. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038065
4. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10e020165 DOI:10.1161/JAHA.120.020165

