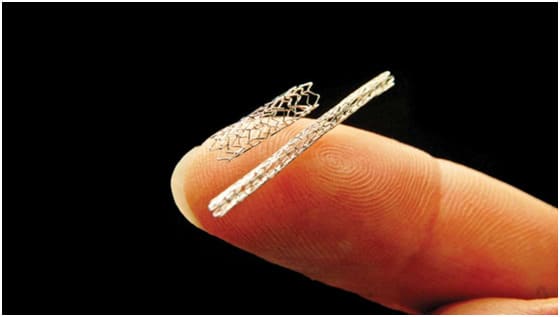
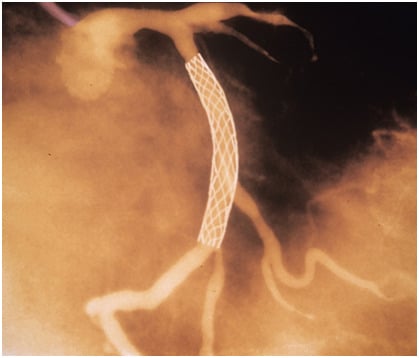
A Coronary Stent is a metallic, hollow and cylindrical mesh used to open up blocked vessels – such as weak or narrow arteries. Stents are often used to treat narrowed coronary arteries that supply the heart with oxygen-rich blood. The stent holds open the narrowed arteries to allow adequate blood to flow to the heart.
What is CAD?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) happens when a waxy substance called plaque builds up on the inner walls of your coronary arteries. This causes your arteries to harden and narrow, decreasing blood flow to your heart. As a result, your heart doesn’t get the blood, oxygen, and nutrients it needs – which can lead to chest pain or a heart attack. CAD often develops over decades. So, you may not know you have a problem until you have a significant blockage or a heart attack.
When is a stent required?
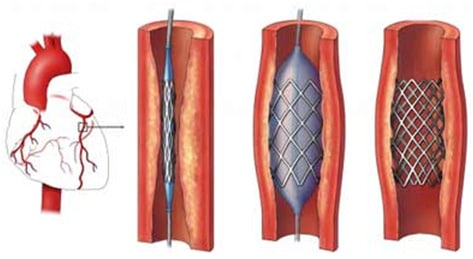
When a blood vessel is blocked by plaque which restricts the flow of blood to the rest of the heart, ballooning and stenting procedures are necessary to help keep the vessel open. Ballooning helps to expand the vessel and the stenting procedure helps keep the artery in position and prevent it from collapsing.
How do coronary stents work?
Coronary stents are small, wire, mesh tubes that help widen a clogged artery and restore adequate blood flow to the heart. During the procedure, your cardiologist will place the stent over a catheter (thin, long tube with a balloon tip) and insert it into an artery in your groin (femoral) or arm (radial). Once the stent reaches the clogged artery, your doctor will inflate the balloon to expand the stent. When the stent reaches the desired size to widen the clogged artery, your doctor will deflate and remove the balloon.
The stent will stay in place permanently to help prop open the artery and decrease its chance of narrowing again. Over time, the inner lining of the artery will grow over the surface of the stent, making it a permanent part of your artery.
Is stent a cure for CAD?
The short answer is no. A stent is not a “cure” for CAD. However, the stent does help treat the problem. The basic function of a stent is to widen the passage of the affected blood vessel in order to restore blood flow.
Results
Coronary
angioplasty greatly increases blood flow through the previously narrowed or
blocked coronary artery. Chest pain generally should decrease. You may be
better able to exercise.
Having
angioplasty and stenting doesn’t mean your heart disease goes away. You’ll need
to continue healthy lifestyle habits and take medications as prescribed by your
doctor.
A stent is,
however, usually the safest option to treat severe CAD in comparison to other
procedures which can be invasive.